Discovering the Amazing World of Pressure Measurement Techniques
Did you know that learning pressure measurement techniques can be the key to the success of many projects? In the engineering world, the proper use of these methods is not only crucial for safety but also for the integrity and quality of projects. Therefore, familiarity with various pressure measurement methods and the ability to use them optimally is essential.
Pressure measurement is fundamental in many processing plants and is often synchronized with temperature control. Hence, having sufficient knowledge in this area can make a significant difference. Now, you can join us as we explore the different types of pressure, related concepts, and the best methods for measuring it.
Let’s journey into the world of pressures and see how we can leverage these powerful tools in our projects. Are you ready? Then let’s get started!
Discovering the World of Pressure: Everything About the Definition and Types of Pressure
Definition of Pressure
Pressure is the force applied uniformly and perpendicularly over a surface. To calculate pressure, you divide the force applied by the area over which it is distributed. The unit of measurement for pressure is Newtons per square meter or Pascals.
In the past, traditional tools like manometers and pressure bulbs were used for measuring pressure. Today, modern and more precise instruments such as pressure data loggers have taken the field, measuring pressure with much greater accuracy.
An interesting point is that if the force applied on a surface remains constant, the smaller the area, the greater the pressure applied. If you are looking to buy a pressure data logger, we recommend visiting the Datis collection, where you can get expert advice to make the best choice.
Types of Pressure
Before delving into pressure measurement methods, it is useful to understand the different types of pressure. Each type is distinguished based on its reference point. Here are the various types of pressure:
- Absolute Pressure: To measure pressure, we need a reference point. Zero absolute pressure is the pressure in a vacuum. This type of pressure, denoted with suffixes like “a” or “abs,” represents the total pressure exerted on a surface.
- Atmospheric Pressure: This pressure is due to the weight of the Earth’s atmosphere up to a height of about 300 miles. Atmospheric pressure decreases with altitude and reaches zero in a complete vacuum. At sea level, atmospheric pressure is approximately 101,325 Pascals, or about 1 bar. With precise instruments, this pressure can be easily measured.
- Gauge and Vacuum Pressure: This type includes the difference between the desired pressure and the ambient pressure. Pressure higher than atmospheric pressure is called positive gauge pressure, while pressure lower than atmospheric pressure is called negative pressure or vacuum. This type is also known as relative pressure.
- Vapor Pressure: This is the pressure exerted by a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases (solid or liquid) in a closed system.
- Partial Pressure of Gases: This is the pressure exerted by an individual gas in a mixture of gases, within the environment or a container.
With the right equipment, you can measure different types of pressure with utmost precision and speed. Now that you are familiar with the world of pressures, are you ready to harness these invisible forces using precise tools and achieve greater efficiency in your projects? Let’s embark on this adventure together!
Introducing Exciting Methods of Pressure Measurement
Are you ready to explore the fascinating world of pressure and its various measurement techniques? We are here to introduce you to the tools and techniques used for measuring pressure. Don’t miss this exciting guide!
1. Measuring Pressure with a Manometer
A manometer is one of the oldest and still most widely used tools for measuring pressure. This simple yet effective device uses a U-shaped tube filled with liquid. Depending on the type of pressure you want to measure, different liquids can be used:
- Absolute Pressure: This method measures pressure relative to a perfect vacuum. Imagine measuring pressure in an environment with no air!
- Gauge or Relative Pressure: In this method, atmospheric pressure is taken as the zero point, and pressure is measured relative to the surrounding environment.
- Differential Pressure: This method measures the difference in pressure between two environments. It’s perfect for determining which side has more flow!
2. Measuring Pressure with a Barometer
A barometer is a tool that allows you to measure atmospheric pressure. This device consists of a thin, sealed metal canister with air removed. As pressure changes, the canister deforms, moving a needle. It’s an old yet still effective method!
3. Measuring Pressure with Elastic Properties
This technique uses the deformation of materials under pressure to measure it. These methods include interesting tools, each with its own story:
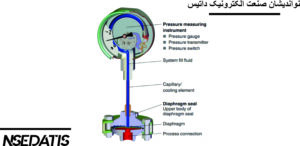
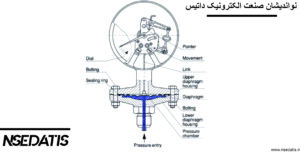
- Diaphragms: Known for their exceptional flexibility for precise measurement.
- Capsules: Metal chambers sensitive to pressure.
- Bourdon Tubes: Curved tubes that deform interestingly under pressure.
- Bellows: Containers that change shape with pressure.
These tools are always valued for their simplicity, strength, and durability.
4. Potentiometric Pressure Measurement
This method uses bellows (accordion-like devices). As pressure increases, the length of the bellows changes, and this change in length is used to measure pressure. It’s a precise and scientific method widely used in many industrial applications.
5. Measuring Pressure with Strain Gauges
Strain gauges are among the most well-known and widely used tools for measuring pressure. When a force such as tension or pressure is applied to an object, it changes length in the direction of the force. This change in length is used to measure pressure. Due to their high accuracy, this method is used in many engineering experiments and projects.
6. Using Capacitive Pressure Sensors
This method uses capacitive sensors. These devices convert pressure into displacement and change the distance between the plates. The change in distance alters the capacitance, and these changes are converted into voltage or frequency corresponding to the pressure. It’s an advanced and precise technique for measuring various pressures.
By selecting the most suitable method and tool for pressure measurement, you can improve the accuracy and quality of your projects. Each of these methods has its characteristics and applications, allowing you to choose based on the project’s needs. Ready to explore the amazing world of pressure with these tools? Let’s embark on this exciting adventure!
Choosing the Right Method for Pressure Measurement: An Exciting and Practical Guide
Are you ready to get acquainted with the amazing world of pressure measurement? If you’re looking for ways to make your projects more accurate and efficient, you’ve come to the right place! Let’s explore the best methods and tips for choosing pressure measurement tools together.
Types of Pressure
- Atmospheric Pressure: The pressure we live in every day! If you want to measure air pressure, you need tools designed for this purpose.
- Hydrostatic Pressure: Used to measure the pressure of liquids, such as in a water or oil tank.
- Dynamic Pressure: Important when measuring pressure caused by the movement of a fluid.
- Static Pressure: For measuring pressure in a stable and unchanging environment.
Measurement Range
Different pressures require different tools. Some instruments work only within specific ranges. For example, manometers are suitable for low pressures, while digital sensors are used for high pressures.
Required Accuracy
Measurement accuracy is crucial for sensitive projects. For instance, even the smallest error can cause issues in the medical industry.
Working Environment
Different environmental conditions require different tools. For example:
- Gaseous, Liquid, or Solid Environments: Tools must be compatible with the type of environment.
- Specific Temperature and Pressure Conditions: Ensure that your tool can operate under these conditions.
Response Time and Speed
The response speed of sensors can be very important. In dynamic projects, you need tools that quickly react to pressure changes.
Protection and Durability
Your tools should be durable. For example, in humid or dusty environments, use water and dust-resistant tools.
Ease of Installation and Maintenance
Nobody wants tools that are difficult to install and maintain. Choosing tools that are easy to install and repair increases efficiency.
Cost
Consider initial and maintenance costs. High-quality tools may be more expensive initially but save money in the long run.
Compliance with Regulations and Standards
Adhering to standards and regulations is crucial. This ensures accuracy and safety and may be mandatory for some projects.
Required Technology and Technical Knowledge
Make sure to get the necessary training for using the tools. Technical knowledge can make a big difference in the quality of results.
Summary
Considering these points and criteria, you can choose the best method and tool for pressure measurement. Novandishan Sanat Electronic Datis offers precision instruments, including flowmeters, pressure data loggers, weather stations, and data transmission systems, to support you in this journey. With Datis equipment, choose the best for your projects and enjoy excellent results!
Ready to complete your projects with high accuracy and quality? Join Datis and select the best equipment. Success awaits you!